
- HOW TO IDENTIFY EXON AND INTRON IN SEQUENCE BIOEDIT HOW TO
- HOW TO IDENTIFY EXON AND INTRON IN SEQUENCE BIOEDIT SOFTWARE
- HOW TO IDENTIFY EXON AND INTRON IN SEQUENCE BIOEDIT DOWNLOAD
- HOW TO IDENTIFY EXON AND INTRON IN SEQUENCE BIOEDIT FREE
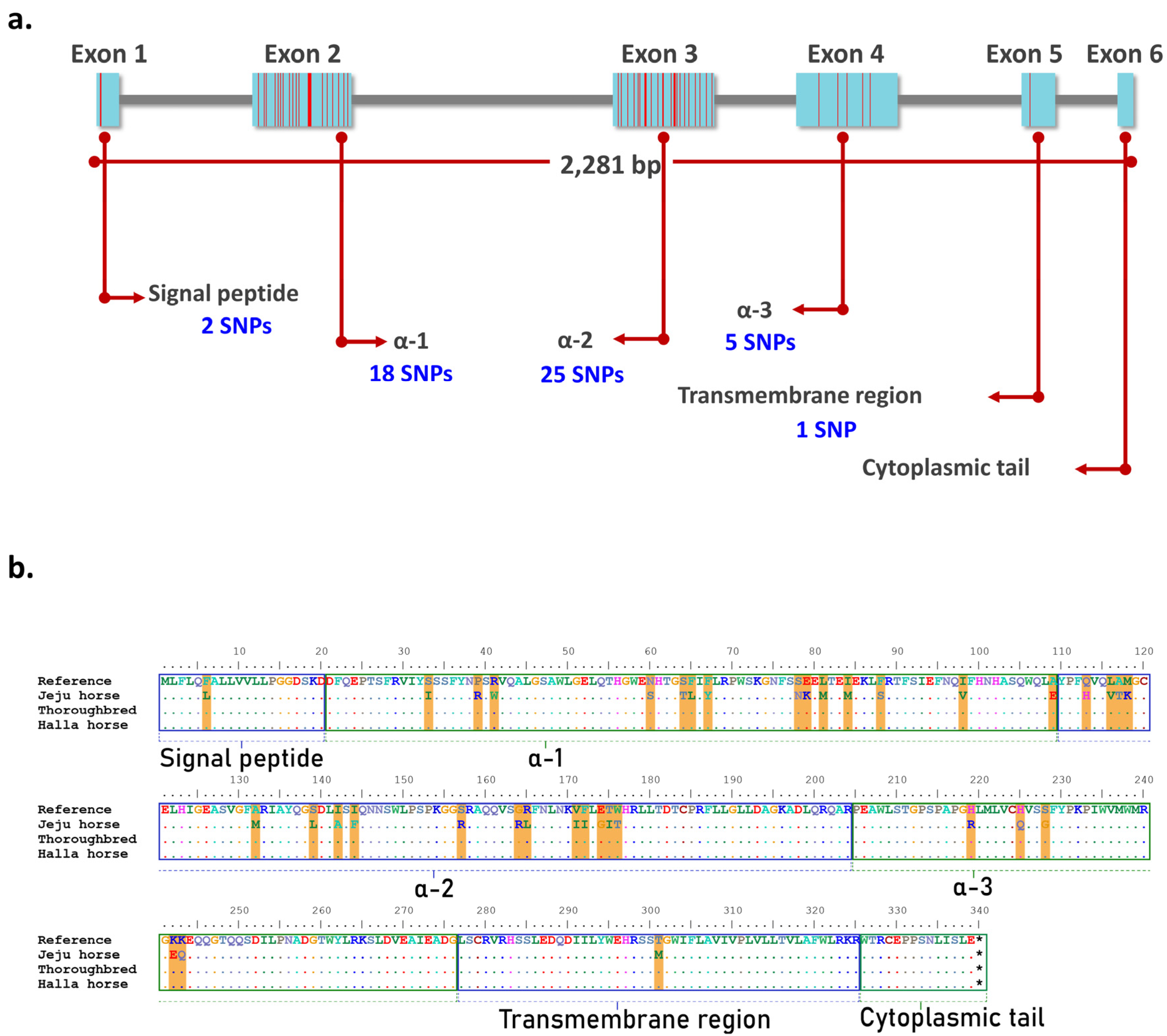
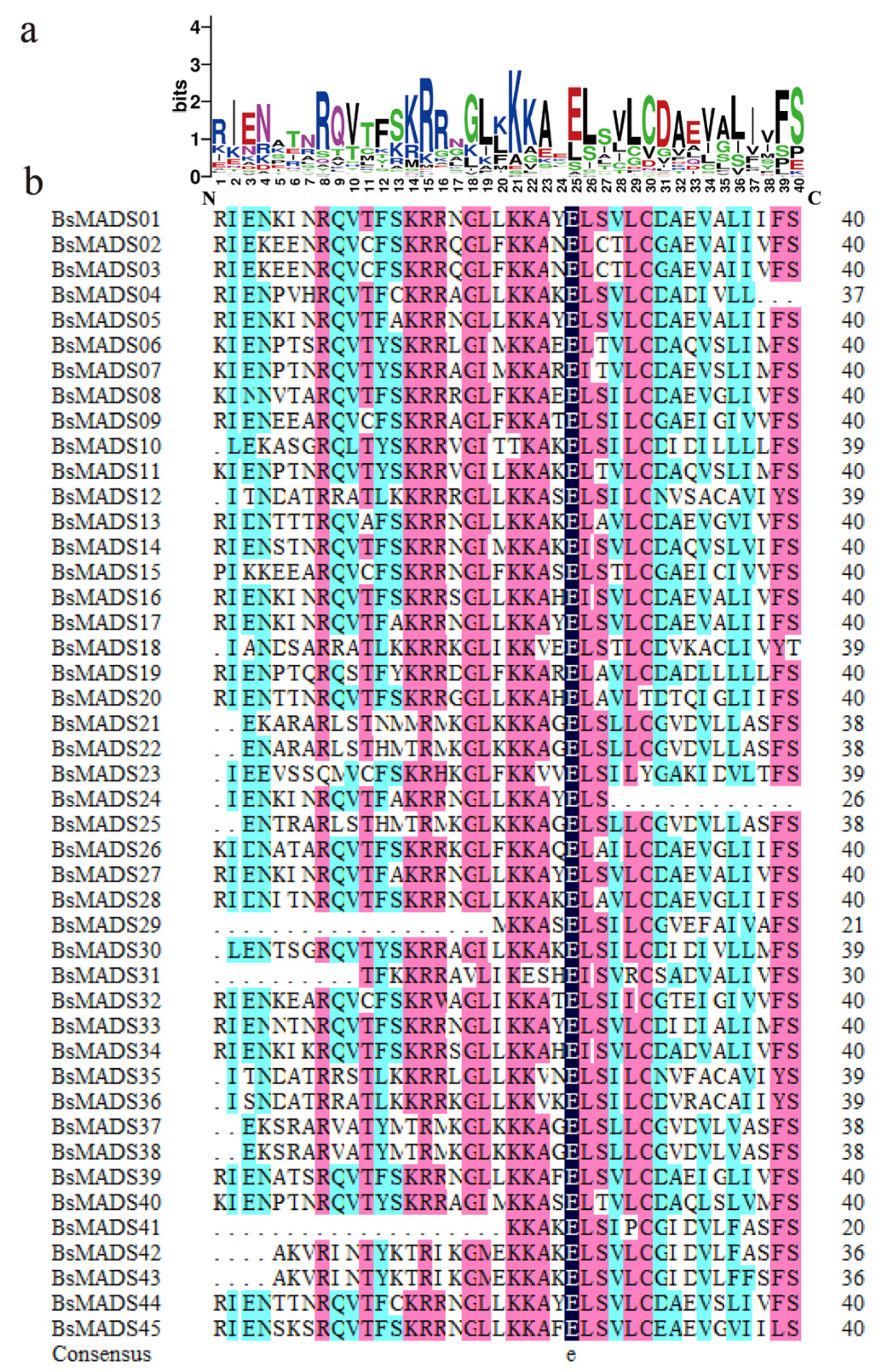
It seems like I need to use compoundLocation, and the locations used in 'join' but I can not figure out how to do it, or find a tutorial. conclusionĪ gene is a segment of DNA that produces a functional product, either a polypeptide or an RNA. The intergenic regions of a gene are composed of introns. This means that a gene in eukaryotes consists of a coding region structure, which is divided into segments called exons Introns can be found between two exons. Introns belong to non-coding DNA.Īll exons together with the intergenic regions are transcribed by RNA polymerase in the primary mRNA transcript. Introns are removed from the primary transcript during mRNA processing. Therefore, a mature mRNA consists only of exons.Įxon splicing can occur in an alternative way in polycistronic mRNAs in prokaryotes, producing more than one type of mature mRNA from a single primary mRNA transcript. Introns in the genome are considered a substantial fraction of the DNA, while exons encode proteins. Therefore, the main difference between introns and exons is their function in the genome. published in 9\10\2017what is the location of exons of any genewhat is the position of introns in that genewhat is the meaning of mRNA join (1. I would like to go through a gene and get a list of 10bp long sequences containing the exon/intron borders from each feature.type 'mRNA'. Introns: The function of introns is not clearly known, but it is considered to be a substantial fraction of the DNA.Įxons: The function of exons is to translate into a protein. Introns: Introns are found in the primary transcription of DNA and mRNA.Įxons: Exons are found in both DNA and mRNA. Using protein blast BlastP (with default settings) find a list. Introns were identified for each gene using the repeat-based alignment in BioEdit in which the 3 end of exon 1 was used to identify the conserved GT splice signal that was approximately 54 nucleotides (nt) from the start codon and the conserved AG splice signal that was located approximately 550 nt from the start codon see. Introns: Sequences in introns are less conserved compared to exons.Įxons: The sequences in the exons are highly conserved. RESCUE-ESE predicts which sequences have ESE activity by statistical analysis of exon-intron and. Introns: Introns remain in the nucleus by splicing the primary mRNA transcript during mRNA processing within the nucleus.Įxons: Exons leave the nucleus towards the cytoplasm after the production of mature mRNA. databases of polinucleotide sequences find homologies. Introns: Introns are only found in eukaryotes.Įxons: Exons are found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Introns: Introns are considered as the bases located between two exons.Įxons: Exons are the bases that encode an amino acid sequence of a protein. Furthermore, programs designed for recognizing intron/exon boundaries for a particular organism or group of organisms may not recognize all intron/exons boundaries. Sequences were manually inspected by BioEdit ver 7.0.9 (Hall, 1999). Introns: Introns belong to non-coding DNA.Įxons: Exons belong to the DNA encoder. Because many genes in eukaryotes are interrupted by introns it can be difficult to identify the protein sequence of the gene. There are a 19 bp deletion at an exon-intron junction and a deletion including the. Introns: Introns are segments of DNA that do not encode any amino acid sequence in the coding region.Įxons: Exons are the segments of DNA that encode a part of an amino acid sequence of a complete protein. Check the CDS feature box to display the CDS feature on the alignments. On the search result page, click the Alignments tab to view pairwise alignments.
To find exon locations on your sequence, follow these steps: Perform a blastn search.

Only exons contribute to the coding region (CDS).
HOW TO IDENTIFY EXON AND INTRON IN SEQUENCE BIOEDIT FREE
NCBI has some basic, but good, tools you can play with.
HOW TO IDENTIFY EXON AND INTRON IN SEQUENCE BIOEDIT SOFTWARE
or 3)use bioinformatic software like macvector or free tools like from NCBI. 2) manually compare a genomic seq verse the cDNA seq.
HOW TO IDENTIFY EXON AND INTRON IN SEQUENCE BIOEDIT DOWNLOAD
Bulk download genome-wide data files with FTP.Every region of DNA has six possible reading frames. Investigating a transcript (splice variant) Once a gene has been sequenced it is important to determine the correct open reading frame (ORF).Searching with a sequence using BLAT or BLAST.Searching Ensembl: An example using a gene name.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
